1. Introduction
Ransomware-as-a-service is a subscription-based model that allows cybercriminals to lease ransomware tools to affiliates, just like a Software-as- a-Service (SaaS) platform.
This article explores how RaaS works, its rise in the cybercriminal underworld History, current active groups, Tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs), notable attacks, company losses, and how businesses can defend against this growing threat.
2. Historical Background
RaaS model appeared in the mid-2010s which Simultaneously with the legitimate business growth of Software-as-a-Service (SaaS).
The first known ransomware attack was the “AIDS Trojan” in 1989, which
encrypted filenames on infected PCs and demanded payment by postal mail. It was rudimentary and targeted individuals.
Families of ransomware like Crypto Locker (2013) and Crypto Wall (2014) emerged, encrypting victims’ files and demanding ransoms payable via Bitcoin.
Around 2015, cybercriminals began adopting a service-based model inspired by legitimate cloud software businesses. Instead of writing ransomware and attacking themselves, skilled developers-built malware toolkits and rented them to affiliates. These affiliates, often with limited hacking skills, could launch ransomware attacks by simply “signing up” and using the provided infrastructure.
This was the true birth of Ransomware-as-a-Service. It lowered barriers to entry, multiplied the number of attacks, and created an underground economy where:
- Developers earn a percentage of every successful
- Affiliates conduct attacks and get the
- Customers (victims) pay ransoms to regain access to their
Expansion and Professionalization (2017–2020)
RaaS platforms grew in sophistication. Developers added features like:
- User-friendly affiliate dashboards
- Automated payment portals
- Negotiation chat systems
- Data leak sites to pressure victims publicly
Groups such as GandCrab, Sodinokibi (REvil), and Conti dominated this era, causing massive damage worldwide.
The Modern RaaS Landscape (2021–Present)
Today, RaaS is a mature industry with dozens of active platforms. New tactics like double extortion (encrypt data + leak stolen info) and triple extortion (adding DDoS attacks) increase pressure on victims.
Law enforcement efforts have disrupted some groups (e.g., Hive in 2023), but the model persists because:
- It’s lucrative — millions in ransoms flow through these
- It’s scalable — affiliates worldwide can
- It’s difficult to eradicate — decentralization and anonymity protect
3. Real -World Incidents & Companies Affected
|
Date |
Organization / Sector |
RaaS Group |
Summary |
Loss (₹ INR) |
News Source |
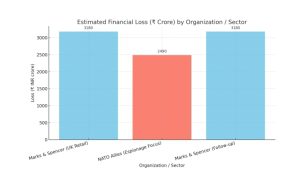
| May 2025 | Marks & Spencer (UK Retail) | Scattered Spider via DragonForce | Phishing-led attack; ~£300 M losses; online
orders/payments disrupted |
~₹3,180 cr (₹10.6B) | The Guardian – MCS link (techinformed. com, theguardian.com, theguardian.com) |
| Oct 2024 | NATO
Allies (Espionage Focus) |
Evil Corp (LockBit affiliate) | Targeted critical infrastructure;
tied to Russian intelligence; extorted over $300 M+ |
~₹2,490 cr (₹24.9B) | Wired – Evil Corp |
| Mar 2025 | Multiple orgs (300+ victims) | Medusa RaaS | FBI/CISA warning on double-
extortion, ransom countdowns |
Not disclosed | AP News – Medusa alert |
| Aug 2024 | University of Paris- Saclay | RansomHouse | TB academic data leaked; university declined to pay | Not disclosed | Le Monde – Paris-Saclay |
| May 2025 | Marks& Spencer (Follow- up) | Scattered Spider + Dragon Force | Confirmation of financial/operational losses via RaaS tools | ~₹3,180 cr (linked earlier) | The Times – MCS gloat mail |
| Apr 2025 | Sam’s Club (US Retail) | Clop | Listed on Clop leak site after Cleo exploit; investigating claim | Not disclosed | Cybersecurity Dive – Sam’s Club |
4. Current Active RaaS Groups
| Group | First Seen | Key Activity in 2025 | Source |
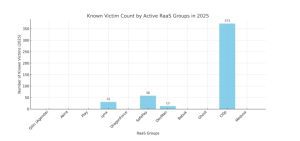
| Qilin (Agenda) | May 2022 | Led April 2025 with most attacks; merged some RansomHub affiliates | Cyble – Apr 2025 |
| Akira | Early 2023 | Consistently high volume in 2025; double extortion on SMEs | Cyble – Apr 2025 |
| Play | Jun 2022 | Among top 5 active in April 2025 | Cyble – Apr 2025 |
| Lynx | Mid 2024 | 31 attacks in April 2025; fast- rising group | Cyble – Apr 2025 |
| DragonForce | 2024 | Continued activity in April–May 2025; LockBit builder reuse | Cyble – Apr 2025 |
| SafePay | Late 2024 | 58 victims in May 2025; notable rise in RDP/VPN-based attacks | Cyble – May 2025 |
| DevMan | 2025 | New entrant; 13 victims in May 2025; uses GPO for mass encryption | Cyble – May 2025 |
| Babuk | Jan 2021 | Re-emerged in March 2025; led incident charts that month | Bitsight – Mar 2025 |
| Ghost | 2021 | FBI/CISA warning in Feb 2025; exploited unpatched public apps globally | Business Insider |
| Cl0p | 2019 | 373 victims in Q1 2025; hit Sam’s Club via Cleo vulnerability | Beazley Q1 2025 Report |
| Medusa | Mid 2021 | Still actively extorting victims in 2025; FBI/CISA advisory (Mar 2025) | CISA Alert |
5. Tactics, Techniques & Procedures
| Group | Tactics | Techniques | Procedures |
|
Qilin (Agenda) |
Initial Access, Execution, Persistence, Defense Evasion, Exfiltration |
– Phishing (T1566)- Exploit Public-Facing App (T1190)- Safe Mode (T1562.009)- Registry Run Keys (T1547.001)- Process Injection (T1055) |
– Custom
Golang/Rust payloads requiring CLI password- Safe Mode execution- Registry modification- Task scheduling- Data leak site |
|
Akira |
Initial Access, Exfiltration, Impact |
– RDP Credential Theft (T1078)- Data Encrypted for Impact (T1486)- Data Staged/Exfiltrated (T1074, T1041) | – Targets SMBs- Uses stolen RDP
credentials- Encrypts data and leaks it on dark web |
|
Play |
Initial Access, Execution, Lateral Movement |
– Exploit External Services- Lateral Tool Transfer (T1570)- Remote Services (T1021) |
– Uses phishing and credential attacks- One of top 5 active groups (April 2025)- Possibly reuses LockBit tooling |
|
Lynx |
Initial Access, Discovery, Encryption |
– Phishing and RDP compromise- File and Directory Discovery (T1083)- Data Encrypted (T1486) | – Fast-growing group- 31 attacks in April 2025- Possibly adopting tools from other RaaS groups |
|
DragonForce
|
Execution, Defense
Evasion, Impact |
– LockBit Builder Use (T1587.001)- Disabling Defenses (T1562)- Data Encrypted (T1486) | – Reused leaked LockBit builder- Focus on extortion and speed- |
|
SafePay |
Initial Access, Exfiltration, Impact |
– RDP/VPN Attack (T1133)- Data Encrypted (T1486)- Data Exfiltration (T1041) |
– 58 victims in May 2025- Rapid rise using RDP/VPN exploitation
Leaks data before encryption |
|
DevMan |
Execution, Impact |
– Group Policy Deployment (T1484.001)- Data
Encrypted (T1486)- Command and Scripting (T1059) |
– Uses GPO to push ransomware
Newcomer with 13 victims (May 2025) |
|
Babuk |
Initial Access, Execution, Exfiltration |
– Exploit App Vulnerabilities- Data Theft and Leak (T1041)- Encryption (T1486) |
– Re-emerged in March 2025- Led attack charts that month
Known for Linux/VMware targeting |
|
Ghost |
Initial Access, Execution |
– Exploit Public Apps (T1190)- Scripting (T1059)- Scheduled Tasks (T1053.005) | – Global exploitation of unpatched web apps
Triggered FBI/CISA alerts in Feb 2025 |
|
Cl0p |
Initial Access, Exfiltration, Impact |
– Exploit Supply Chain (Cleo vuln)- Data Encrypted (T1486)- Data Staged (T1074) |
– 373 victims in Q1 2025- Hit Sam’s Club via Cleo MFT vulnerability- Performs mass data leaks |
|
Medusa |
Execution, Exfiltration, Extortion | – Remote Access Tools- Data Theft (T1041)- Impact (T1486) | – Still active in 2025- Subject of CISA alert (Mar 2025)- Data
leaks via public blog |
6. Conclusion
Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) has turned hacking into a business. Instead of writing their own malware, cybercriminals can now rent ready- made ransomware tools to attack companies and demand money.
These attacks are happening more often in 2025, hitting big names like Marks C Spencer and hundreds of other companies. Hackers steal data, lock systems, and threaten to leak information unless a ransom is paid— sometimes costing businesses millions.
To protect themselves, companies need to stay alert: update software, train employees, back up data, and have a plan in case of an attack. RaaS is growing fast, and the best defence is being ready before it happens.